High frequency waves that are inaudible to the human ear are conveyed to the body tissues in a procedure known as ultrasonography or ultrasound. The echoes are recorded into the form of video or photographic images. Ultrasounds are not merely done to verify a pregnancy or know the gender of the baby; instead it is also performed to diagnose a wide range of disease conditions. Unlike other ultrasound examinations that are done on the surface of the skin only, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed through the insertion of a probe into the vaginal canal. The image produced by this method of ultrasound is high in quality and is a magnified view of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes, the endometrial lining and the adnexal or surrounding areas.
Things you’ll need:
- Bed
- Transducer or Probe
- Condom
- Gel
Steps:
- Study the female genitourinary system.
- Ask the woman to empty her bladder prior to the procedure.
- Instruct the woman to undress from the waist down.
- Assist the woman to lie on the bed with knees bent and feet placed on stirrups.
- Cover the transducer or probe with a condom and apply a gel for lubrication.
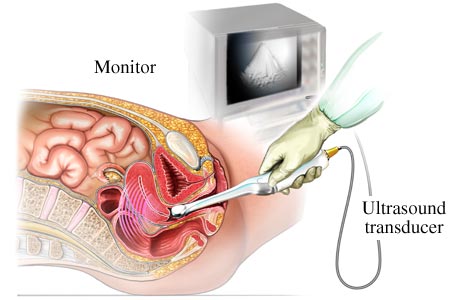
- Insert only two to three inches of the probe into the vagina.
- Allow the probe time to send out sound waves reflective of the body structures.
- Move the probe within the pelvic area to see the underlying structures and organs.
- Identify the anatomical structures and position of the baby. Listen and note the rate and rhythm of the heart.
- Pull the probe slightly back to check the cervix area.
- Check for other potential problems and underlying abnormalities such as an ectopic pregnancy, cancers of the uterus, ovaries or vagina by moving the probe along the pelvic structures.
- Record results and send to radiologist for further interpretation and confirmation.
- Explain to the patient the outcome of the test and point out significant results.
Tips and Warnings:
- It is important to understand and be knowledgeable of the parts of the female genitourinary system to be able to recognize the structures which will be transmitted by the transducer during the transvaginal ultrasound.
- The sound waves will be received by a computer utilizing them to create a picture which will be shown on a TV monitor near the bed.
- Ultrasound examinations are not merely done to detect the growth of a baby inside the womb, it can also be used to detect abnormal growths in the genitourinary system.
- To clearly view the uterus, a saline infusion sonography (SIS) which is a special kind of transvaginal ultrasound is commonly used to locate abnormal masses and estimate their size. This test requires sterile saline solution to be introduced to the uterus prior to the ultrasound. This test is not done on pregnant women.
- A transvaginal ultrasound does not expose a woman to radiation during the test.
- Woman will only feel a mild discomfort during the procedure brought about by the pressure of the probe.